Bio-Chemistry
Proteins are organic compounds that are composed of one or more chains of amino acids. Proteins are the most diverse macromolecules (as we will see later on below). The function of proteins include:
-controlling reatcion rates, and cell processes
-formation of bones
-transport substance (go to cell membrances and allow things to go across)
-Hormones (some lipids and proteins); each proteins has a specific role.
-Protiens translate the DNA's blueprint for the cell to understand.
*Each protein has a specific role.
-
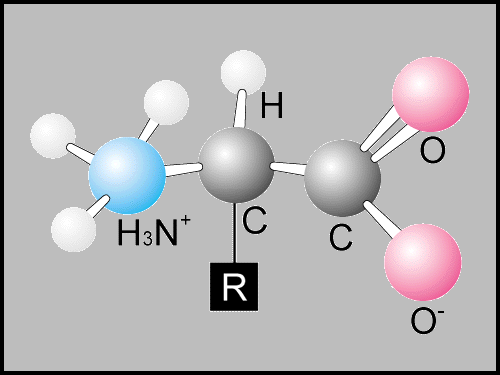
The monomer form of proteins are amino acids (amino acids are compounds with an amino group and a carboxyl group). There are 20 types of amino acids.
-
The polymer form of proteins are polypeptiedes (protein chains)
Proteins are formed through a peptide bond. which is formed though hydrolysis (losing an H2O molceucle). All proteins contain a carboxyl group (COOH) and an amino group (NH2)
*The picture to the right shows a carboxyl group, Amino group, and the formation of a peptide bond
Peptide Bonds
4 levels of organization
There are four levels of protein structures, all listed below:
-
Primary Structure: the specific amino acid sequence-a list of amino acids. Amino acids can be hydrophobic or hydrophilic, basic or acidic (it should be noted that the R-groups are for amino acids to determine if it basic or acidic)
-
Secondary Structure: the repeated folding/coiling patterns in a protein chain that contributes to overall shape. This results from where H-bonding takes place on the peptide backbone. It folds/coils into an alpha helix (α) or beta pleated sheet (β).
-
Teritary Structure: it’s the intricate 3-D shape of a protein that adds a distinct feature to a protein’s secondary structure (based on how the R-groups interact). It determines a protein’s specificity. Hydrophobic interactions and disulfide bridges between the R-groups of amino acids contribute to this shape. Nonpolar amino acids are close together, Van de Waals interactions hold them in place, along with disulfide bridges. Bascially, it results in lots of folding, bending, and looping of the protein.
-
Quaternary Structure: refers to proteins that consist of one or more polypeptide chains, it’s the overall structure, the clustering of multiple peptide chains. The final shape can be fibrous or globular. Polypeptides can be interwinded.
*The picture to the right shows the 4 levels of protein structure.
Denaturation and Chaperonins
-
Denaturation is when a protein unravels and loses it's native shape. This is important because if a protein is denatured, it's biologically inactive. This process can't be reversed, like a cooked egg! Not ideal enviornmental conditions causes bonds to break, therefore changing shape of proteins and affects its ability to function properly.
-
Chaperonins are protein molecules that assist in the proper folding of other proteins-don't specify final structure of the polypeptide. It changes the shape in a way to create a hydrophilic enviornment for folding polypdptides. Chaperonins also mark certain proteins for destruction as well.
R-Groups
R-group properties will determine how the amino acid interact/bond with each other in the tertiary structure. The physical and chemical properties of the side chain (R group) determine the characteristic of an amino acid, which affects its function in a polypeptide. Nonpolar side chains=hydrophobic; polar side chains=hydrophilic. Acidic amino acids usually have negatively charged R group, which is usually ionized. Basic amino acids usually have + side chain. Acidic + Basic R groups=hydrophilic.
*The picture to the right shows polar, nonpolar, acidic and basic proteins.

Protein stucture affecting behavior and function
A functional protein comes from the twists and folds of many polypeptides, all coiled into it’s own unique shape. The amino acid sequence will determine what structure a protein will have. A protein's specific structure will determine how it will work. Usually, a protein’s function depends on its ability to recognize and bind to a certain substance. This property results from its chemical molecular order. The structure is changed by pH or temperature, then it won’t function properly.